Introduction Of Ms PowerPoint
Power point is a presentation software program that is a part of the office package. PowerPoint uses a graphical approach to presentation in the form of slideshows that accompany the oral delivery of the topic. This program is widely used in business and classrooms and is an effective tool when used for training purposes. PowerPoint is presentation software that allows you to create dynamic slide presentations. Slideshows can include animation, narration, images, videos, and much more.
PowerPoint is the one of the simplest computer programs to learn. Microsoft PowerPoint is a software product used to perform computer-based presentations. There are various circumstances in which a presentation is made: teaching a class, introducing a product to sell, explaining an organizational structure etc.Microsoft PowerPoint is a professional presentation program that allows the user to create “presentation slides” that can be displayed on the computer screen or through a projector that is plugged into the computer.
A PowerPoint presentation is a good way to convey pieces of information, usually in the form of an outline, to a large audience.
Five Elements of PowerPoint:-
User Interface
The most visible element of PowerPoint is its user interface—the screens, dialog boxes, buttons, panes, and other parts of the application window. The biggest part of the interface is the pane for creating and editing slides.
Slides
The slide is the PowerPoint element on which you insert text, graphics, audio, video, and animations. You can create new slides by pressing “Ctrl-M” or by clicking “New Slide” on the Home tab. Delete slides by selecting them in PowerPoint‘s left pane and then pressing the “Delete” key. Arrange slides by dragging them in the slide thumbnail pane. Change slide dimensions by clicking the “Page Setup” button on the Design tab.
Content
PowerPoint’s content types include static text and graphics, audio, video, and animation created inside PowerPoint itself. Most of the commands for creating content are on the Insert tab. For example, the Media Clips group has a “Movie” option for importing videos. Use the Animation tab for creating new animations, such as entrance and exit effects on a slide’s graphics and text.
Formatting
Formatting commands are the PowerPoint element with which you decorate the content on your slides. The Home tab, for example, has many of the same formatting commands as Microsoft Word, including character-level tools such as “Bold,” and paragraph-level tools that include “Align Text Left.” Another tab, “Design,” has a group of commands called Themes that let you apply font and color changes to all of the slides in your presentation at once.
Presentation Playback
The final slide presentation will be the only PowerPoint element that your audience sees, if you’ve saved the presentation with the extension PPSX. In that case, clicking the PPSX file brings up the presentation directly, and not the PowerPoint interface you used to create the presentation. But if you’ve saved the presentation with the PPTX extension, the PowerPoint interface will appear—if PowerPoint is installed on the computer. Computers without the main
PowerPoint application can still run PowerPoint presentations by using Microsoft’s free PowerPoint viewer.
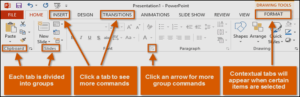
The Ribbon
PowerPoint 2013 uses a tabbed Ribbon system instead of traditional menus. The Ribbon contains multiple tabs, each with several groups of commands. You will use these tabs to perform the most common tasks in PowerPoint.
To minimize and maximize the Ribbon:
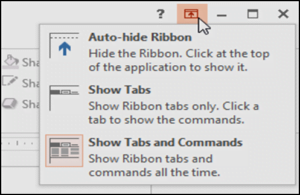
The Ribbon is designed to respond to your current task, but you can choose to minimize it if you find that it takes up too much screen space.
Select the desired minimizing option in the dropdown -menu
Auto hide Ribbon: Auto hide displays PowerPoint in full-screen mode and completely hides the Ribbon. To show the Ribbon, click the Expand Ribbon command at the top of screen.
Show Tabs: This option hides all command groups when not in use, but tabs will remain visible. To show the Ribbon, simply click a tab.
Show Tabs and Commands: This option maximizes the Ribbon. All of the tabs and commands will be visible. This option is selected by default when you open PowerPoint for the first time.
Located just above the Ribbon, the Quick Access toolbar lets you access common commands no matter which tab is selected. By default, it includes the Save, Undo, Repeat, and Start Presentation commands. You can add other commands depending on your preference.
- Click the drop-down arrow to the right of the Quick Access toolbar.
- Select the command you want to add from the drop-down menu. To choose from more commands, select More Commands.
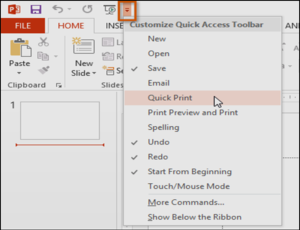
The Ruler, guides, and gridlines
PowerPoint includes several tools to help organize and arrange content on your slides, including the Ruler, guides, and gridlines. These tools make it easier to align objects on your slides. Simply click the check boxes in the Show group on the View tab to show and hide these tools.
To create a new presentation:
- Select the File tab to go to backstage view.
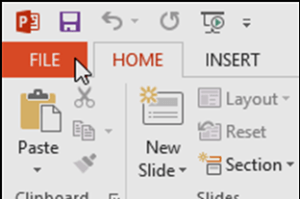
- Select New on the left side of the window, then click Blank Presentation or choose a theme.
- A new presentation will appear.
Save and Save As
PowerPoint offers two ways to save a file: Save and Save As. These options work in similar ways, with a few important differences:
- Save: When you create or edit a presentation, you’ll use the Save command to save your changes. You’ll use this command most of the time. When you save a file, you’ll only need to choose a file name and location the first time. After that, you can just click the Save command to save it with the same name and location.
- Save As: You’ll use this command to create a copy of a presentation while keeping the original. When you use Save As, you’ll need to choose a different name and/or location for the copied version.
Slide Basics:-
PowerPoint presentations are made up of a series of slides. Slides contain the information you will present to your audience. This might include text, pictures, and charts. Before you start creating presentations, you’ll need to know the basics of working with slides and slide layouts.
Understanding slides and slide layouts
When you insert a new slide, it will usually have placeholders. Placeholders can contain different types of content, including text and images. Some placeholders have placeholder text, which you can replace with your own text. Others have thumbnail icons that allow you to insert pictures, charts, and videos.
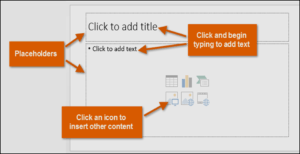
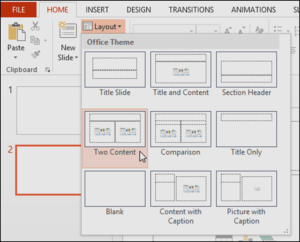
Slides have different layouts for placeholders, depending on the type of information you want to include. Whenever you create a new slide, you’ll need to choose a slide layout that fits your content.
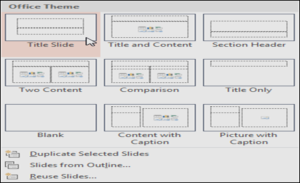
To insert a new slide:
Whenever you start a new presentation, it will contain one slide with the Title Slide layout. You can insert as many slides as you need from a variety of layouts.
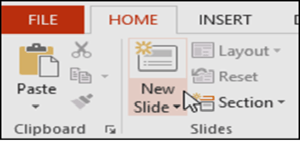
- From the Home tab, click the bottom half of the New Slide command.
- Choose the desired slide layout from the menu that appears.
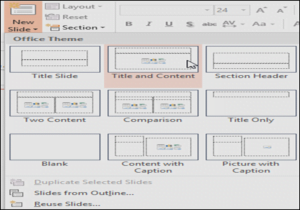
- The new slide will appear. Click any placeholder and begin typing to add text. You can also click an icon to add other types of content, such as a picture or a chart.
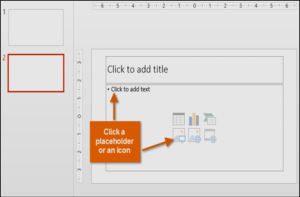
- To change the layout of an existing slide, click the Layout command, then choose the desired layout.
Organizing slides
PowerPoint presentations can contain as many slides as you need. The Slide Navigation pane makes it easy to organize your slides. From there, you can duplicate, rearrange, and delete slides in your presentation.
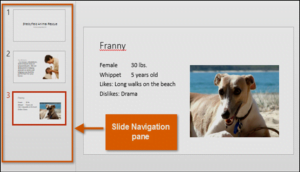
Working with slides
- Duplicate slides: If you want to copy and paste a slide quickly, you can duplicate it. To duplicate slides, select the slide you want to duplicate, right-click the mouse, and choose Duplicate Slide from the menu that appears. You can also duplicate multiple slides at once by selecting them first.
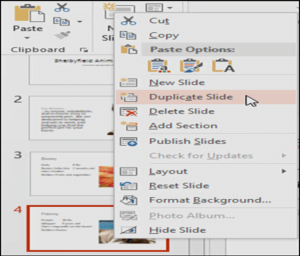
- Move slides: It’s easy to change the order of your slides. Just click, hold, and drag the desired slide in the Slide Navigation pane to the desired position.
- Delete slides: If you want to remove a slide from your presentation, you can delete it. Simply select the slide you want to delete, and then press the Delete or Backspace key on your keyboard
Customizing slides
To change the slide size:
By default, all slides in PowerPoint 2013 use a 16 by 9—or widescreen—aspect ratio. You might know that widescreen TVs also use the 16-by-9 aspect ratio. Widescreen slides will work best with widescreen monitors and projectors. However, if you need your presentation to fit a standard 4-by-3 screen, it’s easy to change the slide size to fit.
To change the slide size, select the Design tab, and then click the Slide Size command. Choose the desired slide size from the menu that appears, or click Custom Slide Size… for more options.

To format the slide background:
By default, all slides in your presentation use a white background. It’s easy to change the background style for some or all of your slides. Backgrounds can have a solid, gradient, pattern, or picture fill.
- Select the Design tab, and then click the Format Background command.
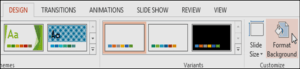
- The Format Background pane will appear on the right. Select the desired fill options. In our example, we’ll use a Solid fill with a light gold color.
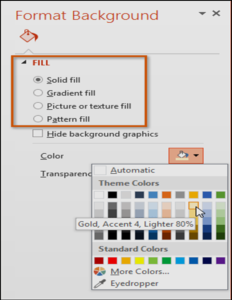
- The background style of the selected slide will update.