Introduction Of Computer
COMPUTER
A computer is an electronic device that manipulates information, or data. It has the ability to store, retrieve, and process data. You may already know that you can use a computer to type documents, send email, play games, and browse the Web. You can also use it to edit or create spreadsheets, presentations, and even videos.

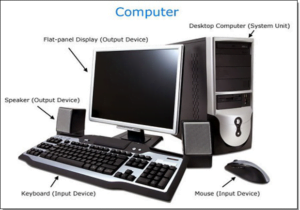
DEFINITION OF COMPUTER:- A computer is an electronic device which is used to perform operation on raw data as per instruction given by user. All the Plugged with computer system( e.g. keyboard, mouse, printer, CPU etc) is called hardware, the language , instruction, data are the called software.
Characteristics or Features of Computer:-
- Speed: A computer is a very fast device. The computer takes a fraction of seconds to perform any operation. The speed of computer is measured in micro seconds (10-3), Milliseconds (10-6), nanoseconds (10-9) and even Picoseconds (10-12).A powerful computer is capable of performing about 3-4 million simple operations per second.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of computer is very high and the degree of a particular computer depends upon its design. But for a particular computer, each and every calculation is performed with the same accuracy. Errors can occur in a computer but these are mainly due to human rather than technological weakness.
- Storage Capacity: Computers can store data and instruction with a lot of volume and very high efficiency.
- Diligence: unlike human being a computer is free from monotony, tiredness, luck of concentration etc. and hence can work for hours together without creating any error. A computer can perform the last calculation with exactly the same accuracy and seed as the first one.
- Versatility: versatility is one of the most wonderful things about the computer. One moment it can do any one operation and next moment if can perform any other operation. A computer is capable of performing almost any task according to given instructions.
Limitation or Drawback of Computer:-
- No I.Q.: Computer is not a magical device. It performs only those works which man can does but the main difference is that computer can work those operations with very high speed and reliable accuracy. It has no any intelligence quality or thinking power
- No Feeling: because computer is only a machine, it has any feeling like human being. It has no brain for thinking as man can does. Man had successes to make computer memory be different inventions of technology but he couldn’t make heart.
- Data Machine Readable: Computer data is read by machine, meaning data obtained from the computer can be read by the computer itself.
- It required power to operate.
Computer Generations:-
First Generation:-
- The period 1940 to 1956, roughly considered as the First Generation of Computer.
- The first generation computers were developed by using vacuum tube or thermionic valve machine.
- The input of this system was based on punched cards and paper tape; however, the output was displayed on printouts.
- The first generation computers worked on binary-coded concept (i.e., language of 0-1). Examples: ENIAC, EDVAC, etc.

Second Generation:-
- The period 1956 to 1963 is roughly considered as the period of Second Generation of Computers.
- The second generation computers were developed by using transistor technology.
- In comparison to the first generation, the size of second generation was smaller.
- In comparison to computers of the first generation, the computing time taken by the computers of the second generation was lesser.

Third Generation:-
- The period 1963 to 1971 is roughly considered as the period of Third Generation of computers.
- The third generation computers were developed by using the Integrated Circuit (IC) technology. In comparison to the computers of the second generation, the size of the computers of the third generation was smaller.
- In comparison to the computers of the second generation, the computing time taken by the computers of the third generation was lesser.
- The third generation computer consumed less power and also generated less heat.
- The maintenance cost of the computers in the third generation was also low.
- The computer system of the computers of the third generation was easier for commercial use.

Fourth Generation:-
- The period 1972 to 2010 is roughly considered as the fourth generation of computers.
- The fourth generation computers were developed by using microprocessor technology.
- By coming to fourth generation, computer became very small in size, it became portable.
- The machine of fourth generation started generating very low amount of heat.
- It is much faster and accuracy became more reliable.
- The production cost reduced to very low in comparison to the previous generation.It became available for the common people as well.

Fifth Generation:-
- The period 2010 to till date and beyond, roughly considered as the period of fifth generation of computers.
- By the time, the computer generation was being categorized on the basis of hardware only, but the fifth generation technology also included software.
- The computers of the fifth generation had high capability and large memory capacity.
- Working with computers of this generation was fast and multiple tasks could be performed simultaneously.
- Some of the popular advanced technologies of the fifth generation include Artificial intelligence, Quantum computation, Nanotechnology, Parallel processing, etc.

Types of Computer:-
There are three basic kinds of computers. This is based on the hardware structure and the way physical quantities are represented in a computer. The following are the three types.
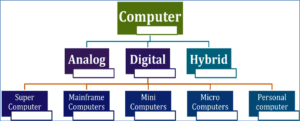
1. Analog Computers
Analog computers are used to process analog data. Analog data is of continuous nature and which is not discrete or separate. Such type of data includes temperature, pressure, speed weight, voltage, depth etc. These quantities are continuous and having an infinite variety of values.
It measures continuous changes in some physical quantity e.g. The Speedometer of a car measures speed, the change of temperature
is measured by a Thermometer, the weight is measured by Weights machine. These computers are ideal in situations where data can be accepted directly from measuring instrument without having to convert it into numbers or codes.
Analog computers are the first computers being developed and provided the basis for the development of the modern digital computers. Analog computers are widely used for certain specialized engineering and scientific applications, for calculation and measurement of analog quantities. They are frequently used to control process such as those found in oil refinery where flow and temperature measurements are important. They are used for example in paper making and in chemical industry. Analog computers do not require any storage capability because they measure and compare quantities in a single operation. Output from an analog computer is generally in the form of readings on a series of dial (Speedometer of a car) or a graph on strip chart.
2.Digital Computers
A Digital Computer, as its name implies, works with digits to represent numerals, letters or other special symbols. Digital Computers operate on inputs which are ON-OFF type and its output is also in the form of ON-OFF signal. Normally, an ON is represented by a 1 and an OFF is represented by a 0. So we can say that digital computers process information which is based on the presence or the absence of an electrical charge or we prefer to say a binary 1 or 0.
A digital computer can be used to process numeric as well as non-numeric data. It can perform arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division and also logical operations. Most of the computers available today are digital computers. The most common examples of digital computers are accounting machines and calculators.
The results of digital computers are more accurate than the results of analog computers. Analog computers are faster than digital. Analog computers lack memory whereas digital computers store information. We can say that digital computers count and analog computers measures.
3. Hybrid Computers
A hybrid is a combination of digital and analog computers. It combines the best features of both types of computers, i-e. It has the speed of analog computer and the memory and accuracy of digital computer. Hybrid computers are used mainly in specialized applications where both kinds of data need to be processed. Therefore, they help the user, to process both continuous and discrete data. For example a petrol pump contains a processor that converts fuel flow measurements into quantity and price values. In hospital Intensive Care Unit (ICU), an analog device is used which measures patient’s blood pressure and temperature etc, which are then converted and displayed in the form of digits. Hybrid computers for example are used for scientific calculations, in defense and radar systems.
Classification of Digital Computer
Supercomputer
The most powerful computers in terms of performance and data processing are the Supercomputers. These are specialized and task specific computers used by large organizations. These computers are used for research and exploration purposes, like NASA uses supercomputers for launching space shuttles, controlling them and for space exploration purpose. The supercomputers are very expensive and very large in size. It can be accommodated in large air-conditioned rooms; some super computers can span an entire building.

Uses of Supercomputers
Space Exploration
Supercomputers are used to study the origin of the universe, the dark-matters. For these studies scientist use IBM’s powerful supercomputer “Roadrunner” at National Laboratory Los Alamos.
Earthquake studies
Supercomputers are used to study the Earthquakes phenomenon. Besides that supercomputers are used for natural resources exploration, like natural gas, petroleum, coal, etc.
Weather Forecasting
Supercomputers are used for weather forecasting, and to study the nature and extent of Hurricanes, Rainfalls, windstorms, etc.
Nuclear weapons testing
Supercomputers are used to run weapon simulation that can test the Range, accuracy & impact of Nuclear weapons.
Mainframe computer
Although Mainframes are not as powerful as supercomputers, but certainly they are quite expensive nonetheless, and many large firms & government organizations uses Mainframes to
run their business operations. The Mainframe computers can be accommodated in large air-conditioned rooms because of its size. Super-computers are the fastest computers with large data storage capacity, Mainframes can also process & store large amount of data. Banks educational institutions & insurance companies use mainframe computers to store data about their customers, students & insurance policy holders.

Minicomputer
Minicomputers are used by small businesses & firms. Minicomputers are also called as “Midrange Computers”. These are small machines and can be accommodated on a disk with not as processing and data storage capabilities as super-computers & Mainframes. These computers are not designed for a single user. Individual departments of a large company or organizations use Mini-computers for specific purposes. For example, a production department can use Mini-computers for monitoring certain production process.

Microcomputer
Desktop computers, laptops, personal digital assistant (PDA), tablets & smart phones are all types
of microcomputers. The micro-computers are widely used & the fastest growing computers.
These computers are the cheapest among the other three types of computers. The Micro-computers are specially designed for general usage like entertainment, education and work purposes. Well known manufacturers of Micro-computer are Dell, Apple, Samsung, Sony & Toshiba.
Desktop computers, Gaming consoles, Sound & Navigation system of a car, Notebooks, PDA’s, Tablet PC’s, Smart phones, Calculators are all type of Microcomputers.

PC (Personal Computer)
Stands for “Personal computer.” PCs are are what most of us use on a daily basis for work or personal use. A typical PC includes a system unit, monitor, keyboard, and mouse. Most PCs today also have a network or Internet connection, as well as ports for connecting peripheral devices, such as digital cameras, printers, scanners, speakers, external hard drives, and other components.

Desktop Computer
A Desktop is commonly referred to as a physical computer unit, as well as a graphical user work space on a software operating system like the Windows Desktop. This article compares the Desktop computer to the Laptop computer units.
The most common components of a Desktop is the computer terminal powered by a grounded electrical source i.e. a wall socket. To be fully functional, the Desktop is connected to an external monitor, keyboard, and mouse via Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or USB, HDMI, and VGA cable connections.

If the Desktop is not configured for WiFi, Bluetooth, or has the necessary ports for USB or HDMI, these would have to be installed manually, probably at an additional cost as the average user may not necessarily have the technical know-how to set this up.
The default factory specifications vary and there are enough choices out there to suit different consumer needs, starting from entry-level computers with smaller hard drives and lower processing power to high spec computers used for gaming, multimedia design, or as servers.
Having separate parts connected to make up the Desktop unit means it is not easily transported between office and home, or easily used while traveling (if at all possible), so Desktops usually reside in a permanent place.
A Laptop (also known as a Notebook), is an all-in-one computer that uses batteries or AC power that can last for several hours. Unlike the Desktop, the Laptop computer is easily transported and can be used as long as the battery lasts.
However it is becoming very common for public places to have powering units available for phones and Laptops so they can be used almost everywhere!
Laptops come in various sizes with various specifications. Like the Desktop, the type of computer depends on the consumer needs.
A Laptop has a built-in monitor, keyboard, and typically a touchpad (or trackball). External peripherals can also be connected using different cable connections, depending on what ports are provided by manufacturer. Essentially, the Laptop can be used as a fully functional unit without any connected devices or power.
As technology advances, the Laptop is becoming more popular with the average consumer and the preferred computer for business users, especially those who travel for work.
Similarities
- Most Desktops and Laptops are sold with pre-installed software and operating systems like Windows 7, or if it is an Apple computer, then the Mac OS.
- Both computer units come with port connections (varying between each make and model), and a built-in CD/DVD component, however this is being phased out in some of the newer Laptop models.
- Peripheral devices can be connected such as external hard drives, printers, cameras, and phones, etc.
- For both the Desktop and Laptop, key specifications to consider before purchasing is
- CPU
- Memory (RAM)
- Hard drive capacity
- Graphics card.
- These specs determine the computer’s limits so if video production is the primary task and the computer has a low end graphics card, then the computer (laptop or desktop) will not be well suited for the job.
The Main Difference Between Desktop and Laptop
The biggest and most noticeable difference is the Desktop needs basic external devices to be fully functional, whereas the Laptop has all necessary devices built-in, making it the most portable.
Mobility
- A Desktop stays in the office or home and needs the computer terminal to be connected to an external monitor, keyboard, and mouse; whereas the Laptop has the built-in components and thus easily transported as one complete device that can be used in most environments.
Power
- The Laptop can run off AC power, batteries, or mains power, whereas the Desktop can only run off the main powers. It is not manufactured for any battery use.
- The Laptop battery has improved over time, and can last up to several hours, depending on how much processing power is being used and keeping Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connections open, increases the battery power consumption.
Speed
- Although the Desktop and the Laptop are becoming more equal in terms of speed and performance specifications, the Desktop still remains as the more powerful choice for activities such as gaming and video production.
Buying a Gaming Laptop with similar specs to a Gaming Desktop would be at a much higher
price than a Gaming Desktop.
- If the computer is needed for basic office processing, internet usage, and photo viewing, then a standard Laptop would be perfectly suitable.
Specifications
Generally, Laptops are known to have lower specs than Desktops, as there is a compromise on size and portability, vs performance and speed.
Screen size
- Desktop monitors can vary from small 15 inch screens to larger ones such as the 34 inch. Laptops have built-in screens which also have varying sizes.
- The larger the screen, the larger and heavier the Laptop, however if a small Laptop is purchased for easy mobility, it can be connected to a larger external monitor if possible.
- If connecting an external monitor to a Desktop computer that permanently stays in one place, then the size of the monitor would not be a restrictive factor as it is setup once and not necessarily moved so the weight is not an issue.
Storage, Memory and Data
- For storing very large amounts of data, the Desktop computer would be a better choice and if needed, additional memory can be added to improve performance, or the hard drive can be replaced. Laptops cannot be so easily expanded as the Desktop.
- Backups are recommended for all data, whether it resides on a Desktop or Laptop, however if using a Laptop is would be essential to have backups as the risk of losing data increases with mobility due to theft, loss of computer, physical damage (dropping the computer), etc.
Summary
Although Laptops are becoming more highly spec’s and configured for performance, the Desktop still has the upper hand. Besides budget, the biggest deciding factor would be Performance or Portability.
| Area | Desktop | Laptop |
| Portability | Desktops need external devices to be fully functional thus making it cumbersome to constantly move or transport a the computer. It usually resides in one place.
| Laptops are highly portable as a complete all-in-one purpose device making them easily transportable. |
| Performance | Desktop processors have always led the way with larger processors making them more powerful than Laptops. | Laptop processors are catching up to the Desktop but they still have size limitations to fit with portability. |
| Ease-of-use and assembly | Desktops need to be manually setup by connecting the necessary devices while avoiding cable chaos and they require larger work areas than Laptops. | Laptops simply need to be powered and opened before being ready for use. There is little to no effort for a basic setup. |
| Cost | Entry-level Desktops are relatively affordable for most consumers. There is a large variety of peripheral devices available at additional cost but most packages are cheap enough for the average household. | Entry-level Laptops have a higher starting price than Desktops. The higher the specs, the higher the cost which can increase considerably for Laptop models. |
| Monitor and Keyboard | There are no limitations to the size and weight of external devices as the Desktop is not intended for portability. | The size of the screen and keyboard determine the size and weight of the laptop, which needs to be considered as it is intended for portability. |
| Upgrading | Components within the Desktop computer (terminal) can be removed and replaced and in most cases allows easy upgrading of storage capacity, memory, graphics controller, etc. | In Laptops, only the hard drive and memory can be replaced, but other cards and components cannot be removed. To upgrade any other aspect, would require purchasing a new Laptop. |
| Maintenance and Repairing | It is a lot simpler to fix components in a Desktop computer as it allows the removal and replacement of many parts available from most computer hardware stores. | Because of the compact design and non-removal of most components in a Laptop, it requires technical expertise to repair. |
| Gaming | Desktops are considered more powerful for Gaming as the graphics and video cards can be top end with no limitations on power consumption and more than one video card can be installed. | Laptops are limited to space so limits the size of some components. Gaming Laptops do have above average specs but they are still limited to space to keep them portable. The power consumption on an unplugged Laptop will increase drastically with gaming activities. |

