Introductory concepts of Programming
Introduction
To obtain the solution of a program, one must think and come up with a suitable step by step procedure. The problem may be solved skillfully by following the procedure either by a human or by a computer. In computer form, it is a step by step procedure in a proper sequence which is also called as a program and systematic notations for these sequences of step by step procedure is known as programming language. The task of developing programs for the solution of computational problems is known as programming and the person who is involved in doing programming is known as a programmer.
Computer Programming
Computer programming is the process of writing, testing and maintaining the source code of computer programs. The source code is a code which is written in a programming language i.e. source language. The source language may be any high language which is easily understandable by the user of the language.
The task of developing programs for the solution of computational problems is known as computer programming.
Programming Concepts
There are many different languages that can be used to program a computer. The most important of these is machine language.
Machine language is a collection of sequence of instructions written in the form of binary numbers consisting of 0’s and 1’cito which computer responds directly. This is the natural way to interact with computer.
Very few computer programs are written in machine language because of two significant reasons: First, because machine language is very difficult to work with and second, because every different type of computer has its own unique instruction set. Thus a program written for one type of computer in machine language cannot be run on another computer without some alteration .So it is not portable.
A computer program will be written in some high level; language which is very much similar and compatible with human languages. A program that is written in a high level language must be translated into machine language before execution. This process is known as compilation or interpretation. Compiler translates the entire program into machine language before executing any instructions. Interpreters on the other hand translate and execute single instruction at a time. A compiler or interpreter is itself a computer program .It accepts high level language (e.g. C) program as an input and generates a corresponding machine language programs an output. The original high level program is known as source code or source program and the resulting machine language program is known as object code or object machine language.
Programming Languages
To write a program, a standard programming language is used. A programming language is composed of a set of instructions in a language understandable to the programmer and recognizable by a computer.
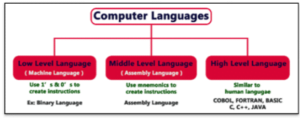
Programming language can be classified as:
- Low Level Language
- Assembly Level Language
- High Level Language
Low Level Language
A low level computer language is one that is closer to the language of the computer, which is 1’s and 0’s.
Machine Language
This is a sequence of instructions written in the form of binary number consisting of 1’s and 0’s to which computer responds directly. The machine language is also referred as the machine code. Machine languages are the only languages understood by computers.
Advantages of Low Level Language
- Machine language makes fast and efficient use of the computer.
- It requires no translator to translate the code. It is directly understood by the computer.
Disadvantages of Low Level Language
- It is almost impossible to find and correct errors.
- Time taking
- Costly
- Difficult to program.
Assembly Language
An assembly language is a low-level programming language designed for a specific type of processor. It may be produced by compiling source code from a high-level programming language (such as C/C++) .Its code can be converted to machine code using an assembler.
An assembler is a translator that takes input in the form of assembly language program and produces the machine language code as its output. Assembly language is just one level higher than machine language.
Advantages of Assembly Language
- The symbolic programming of Assembly Language is easier to understand and saves a lot of time and effort of the programmer.
- It is easier to correct errors and modify program instructions.
- Assembly Language has the same efficiency of execution as the machine level language.
- Readability in assembly language is much more than the machine language.
Disadvantages of Assembly Language
- Programming is difficult and time consuming.
- There are more chances for errors debugging and verifying assembly code is difficult.
- It’s difficult to port from assembly language to other languages.
High Level Languages
High level language has instructions that are similar to human language. It has a set of grammar that makes it easy for a programmer to write the programs. It is easy to bug and debug the programs. This language is very close to English language and is called as third generation Language. HLL is BASIC, COBOL, FORTRAN etc.
Advantages of High Languages
- Readability program written in these language are more readable than those written assembly and low level language.
- Portability HLL can run on different machine with little or no change.
- Easy debugging error can be easily detected and removed.
- The command of this programming language is closer to English language. So software can be easily developed.
Low Level Language Vs High Level Language
| Low Level Language | High Level Language |
|
|
Concepts Related with The Execution of Program
Compiler:-
It is software which helps to translate a high level language program into the machine language.
It takes the source code as input and produces the machine language code for the machine on which it is to be executed as output.
Interpreter:-
It is also software that translates the high level language program into the machine level language. The compiler and interpreter have different approach of translation. It translates and executes the program line by line.
Compiler Vs Interpreter
| Compiler | Interpreter |
|
|
|
Types of errors that occur in a computer program:
An error is something you have done which is considered to be incorrect or wrong, or which should not have been done. While writing c programs, errors also known as bugs in the world of Programming may occur unwillingly which may prevent the program to compile and run correctly as per the expectation of the programmer.
- Syntax Error
- Semantic Error
- Run Time Error
Syntax Error (Compile Error)
Syntax errors occur in the programs, when the rules or syntax of the programming language is not followed.A syntax error is an error in the source code of a program. For example, a missing semicolon at the end of a line or an extra bracket at the end of a function may produce a syntax error.
Such programming errors are due to:
- Incorrect Punctuation
- Incorrect word sequences
- Undefined Terms
- Misuse of terms
Semantic Error (Logical Error)
A logical error is one that may compile or run, but produces an unexpected result. When a logical error occurs, the computer does not print the correct output. The computer does not tell you what wrong .For example is if you want to multiply two variables. A semantic error is also called a “logical error”.
Y=AB
But by mistake you have written it as
Y=A+B
This error will not be detected by the language processor since no language rules have been broken. However the output will produce wrong results.
Run Time Error (Execution Error)
Run time error occurs when a program is executed on a computer and the result is not achieved due to some misinterpretation of a particular result. This could be something like dividing a number by zero which results in a very large value of quotient. It may be another instruction which a computer is not able to understand.
#include<stdio.h>
main () {
int x = 52;
int y = 0;
Printf (“Div: %f”, x/y);
}
Program crashes during runtime.

