Introduction to C
Introduction
C is a general-purpose high level language that was originally developed by Dennis Ritchie for the UNIX operating system in 1970’s at AT &T’s Bell laboratories of USA.C seems to very popular because it is reliable ,simple, easy to use and portable. Programs written in C language are fast and very efficient.
Historical Development of C
By 1960’s many computer languages exists but each has been developed for a specific purpose .e.g. COBOL for business and commercial applications, FORTRAN for engineering and scientific purposes etc.
The C language derives its name from the fact that it is based on a language developed by Ken Thompson, another programmer at Bell laboratories. He adapted it from a language known as Basic Combined Programmi9ng Language (BCPL).To distinguish his version of language from BCPL ,Thompson named it B language, which was the first letter of BCPL. When the language was modified and improved to its present state, the second letter of BCPL,C was chosen to represent the new version by Dennis Ritchie.
Where C stands:
High Level Languages or Problem oriented Languages The languages which are designed to give better programming efficiency that also means faster program development e.g. BASIC, FORTRAN, COBOL, PASCAL etc.
Low Level Languages or Machine Oriented Languages The languages which are designed to give better machine efficiency which also means faster program execution. E.g. Assembly language and machine language.
Importance of C language/Characteristics
C is one of the most popular and important programming language nowadays used in any application area due to its various qualities.Ca programming language look like English language, so the difficult and more complex programs can be written in a very simple and easier way.
- As a middle-level language, C combines the features of both high-level and low-level languages. It can be used for low-level programming, such as scripting for drivers and it also supports functions of high-level programming languages, such as scripting for software applications etc.
- C is a structured programming language which allows a complex program to be broken into simpler programs called functions. It also allows free movement of data across these functions.
- C language is case-sensitive which means lowercase and uppercase letters are treated differently. Almost everything in C program is written in small case.
- C has the characteristic of portability .Portable means independent. The program made in C on one computer can be run on different computers by not changing anything, thus increasing the efficiency of the language.
- C is a general-purpose programming language and can efficiently work on enterprise applications, games, graphics, and applications requiring calculations, etc.
- C language has a rich library which provides a number of built-in functions. It also offers dynamic memory allocation.
- Modularity of C language makes it very popular modular means the program made in C can be easily divided into small modules with the use of functions.
- C language has only 32 keywords. So becomes easy to separate them from the variable names because keyword can’t be a variable name. So there is less restriction for a variable name in C.
Desirable Program Characteristics
Before writing any program let us discuss some important characteristics of well-written computer programs. These characteristics can be used for writing programs in any programming language, not only C.
Clarity: Clarity refers to the overall readability of the program. The program should be written clearly. If it is clearly written, it should be possible for another programmer to follow the logic of the program without undue effort.
Accuracy: The calculations of the program should be accurate. All other properties of the program will be meaningless if calculations are not carried out correctly.
Simplicity: The clarity and accuracy of a program are enhanced by keeping things as simple as possible and consistent.
Modularity: Programs can be broken down into a series of subtasks. These subtasks can be called as modules. In order to increase the clarity and accuracy of the program, breaking down the program into small modules is known as modularity.
Basic Structure of a C Program
The components of the basic structure of a C program consists of 7 parts
- Document section
- Preprocessor/link Section
- Definition section
- Global declaration section
- Function declaration section
- Main function
- User-defined function section
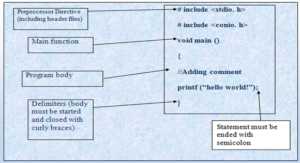
Parts of C program
- # include <stdio.h> – This command is a preprocessor directive in C that includes all standard input-output files before compiling any C program so as to make use of all those functions in our C program.
- int main() – This is the line from where the execution of the program starts. The main() function starts the execution of any C program.
- { (Opening bracket) – This indicates the beginning of any function in the program (Here it indicates the beginning of the main function).
- /* some comments */ – Whatever is inside /*——-*/ are not compiled and executed; they are only written for user understanding or for making the program interactive by inserting a comment line. These are known as multiline comments. Single line comments are represented with the help of 2 forward slashes “//——”.
- printf(“Hello World”) –The printf() command is included in the C stdio.h library, which helps to display the message on the output screen.
- getch() – This command helps to hold the screen.
- return 0 –This command terminates the C program and returns a null value, that is, 0.
- } (Closing brackets)- This indicates the end of the function. (Here it indicates the end of the main function)
We have to follow some rules while writing statements in a C program. These rules are:
- As C is a case sensitive language so usually all the statements are entered in small case letters
- In assessment two words must be separated by blank spaces to increase the readability of the statements.
- Every statement in C ends with a semicolon;
The First Simple C Program
Example :Write a program to calculate sum and product of two numbers.
/*Program to calculate sum and product of two numbers*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
Void main()
{
int a, b, sum, prod;
printf(“\n Enter two numbers “);
scanf(“%d %d”, &a, &b);
sum = a + b;
prod=a*b;
printf(“\n sum of two numbers=%d”, sum);
scanf(“\n product of two numbers=%d”,prod);
getch();
}
Output:
Enter two numbers 4 6
Sum of two numbers=10
Product of two numbers=24
Explanation
- The first line is comment line which is used to tell the purpose of the program.
- Second line is the inclusion of a special file (stdio.h)i.e.(standard input output header file )which contains information that must be required to compile or run a program. It contains details of input (scanf)and output(printf)functions.
- In the third line, the program actually starts with the main() function.
- Remaining lines which are present in({) starting brace and (})closing brace are the compound statements which includes variables decelaration,output statements (printf)input statements (scanf),assignment statements etc.(which may vary in another program).

